How much protein do you need?
-
30% protein on a 2000kcal is 150g of total protein, while
-
30% protein on a 3000kcal diet is 225g!
Nuancies of Plant Proteins
-
Their amino-acid profile.
-
Macronutrient composition of protein rich plant and animal foods
Amino Acid Profile
| Food | Amino Acid Score | PDCAAS | True protein Digestibility (%) |
| Wheat Flour | 0.47 | 0.43 | 92.3 |
| Lentils | 0.71 | 0.63 | 87.9 |
| Lentil: Wheat (25:75 Blend) | 0.78 | 0.71 | 91.0 |

Macronutrient composition
-
You will feel bloated due to all the extra fiber intake
-
You will have trouble eating enough for your high energy demands
-
You might be getting high protein, but still lack certain amino-acids to effectively build or maintain muscle mass.
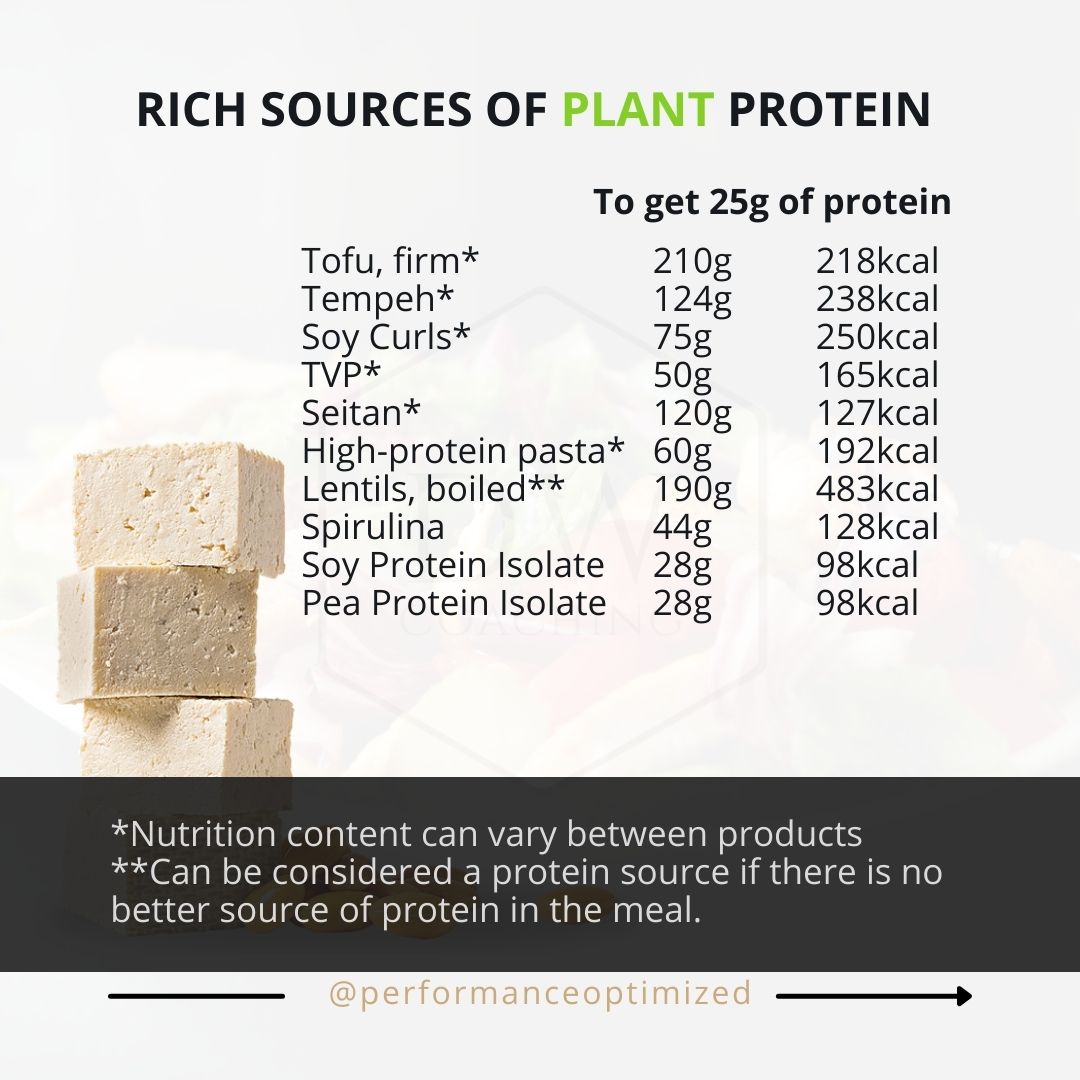
Increasing plant protein intake
Make Pulses Staples of your diet
Grains Higher in Protein
High Protein Vegetables
Let’s not forget bout vegetables that are high in protein. Including some of these in your meals can boost your total protein intake but I would not replace leafy green vegetables that are nutrition powerhouses amd people already have problems eating enough of them.
Which vegetables are high in protein?
Broccoli, green peas, edamame beans, mushrooms (although not technically vegetables), spaghetti squash, corn, potatoes.
High Protein Seeds
Seeds are essential sources of fats on a plan-based diet. If you want to boost protein, choose hemp seeds, chia seeds, pumpkin seeds, and peanuts (although technically legume).
For better mineral absorption, grind the seeds before eating or grind and store in an air-tight container in a cold place for up to a week.
Other plant protein sources
Nutritional yest, vegetable burgers (read nutrition labels, some are high in fat and low protein), faux meat, spirulina. Plant protein powders can be your best friend as you can include them in cooking and baking!
|
Breakfast
|
Lunch
|
Dinner
|
|
Oatmeal with hemp seeds, plant milk and fruit
|
Split peas dhal + Rice
|
Hummus with vegetables
|
|
Whole-wheat bread with hummus
|
Bean goulash with sourdough bread
|
Vegetables salad with apples, legumes and quinoa
|
|
Tofu with greens and sweet potato
|
Whole-wheat pasta with tomato sauce and tempeh
|
Whole-wheat toasts with avocado and smoked tofu
|
|
Chia pudding with banana and peanuts
|
Whole-wheat burrito with legumes and vegetables
|
Oat cakes with raisins, peanuts, plant milk
|
High-protein Vegan Meal Plan
How are you supposed to eat all these beans and legumes without digestive issues?
-
Eat slowly – when we rush at a meal, we may activate our sympathetic nervous system, which induces the “fight or flight” response and can mess with digestion. By staying calm and eating slowly, we’re more likely to stay in the parasympathetic “rest and digest” state.
-
Add beans and legumes gradually and variety – your digestive track needs to get used to higher fiber intake. There are different strains of bacteria involved in processing different food.you might find that chickpeas are OK but beans aren’t
-
Consider preparation – you may find out that beans and legumes prepared in certain way are better tolerated. Rinse, soak, pressure cook for the best effect.
-
Digestive enzymes Alpha-galactosidase is an enzyme that helps to break down the bloat-inducing starch in beans.
-
Include more processed sources of plant protein. It will ease digestion, reduce fiber, and bloating and gas.
- Water – beans, lentils, and whole grains contain a lot of fiber. Fiber pulls in water and if you don’t drink enough, it will keep stuck in your digestive track.
